人工智能中的编程 - 第2章: 并行编程(Parallel Programming)
并行编程(Parallel Programming)
如何加快计算的速度?
- 提高时钟频率
- 使用并行计算
使用并行计算的原因:时钟频率不能无限制地提高,存在功耗和热量问题。
CPU和GPU的区别:
- CPU(中央处理器):适合处理复杂的任务,具有较少的核心,但每个核心都很强大。优化时延(Latency)。
- GPU(图形处理器):适合处理大量简单的任务,具有大量的核心,但每个核心相对较弱。优化吞吐量(Throughput)。
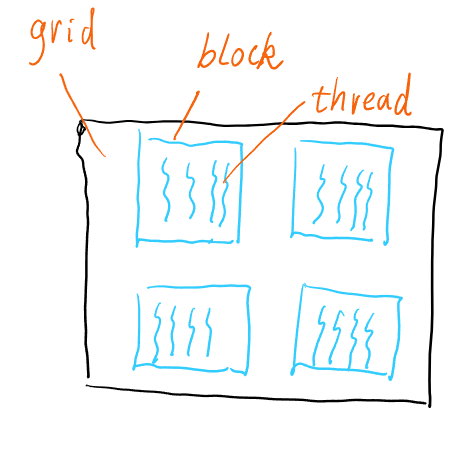
CUDA
在CUDA编程模型中,程序被分为主机代码(Host Code)和设备代码(Device Code)。
- 主机代码在CPU上运行,负责管理内存和启动设备代码。
- 设备代码在GPU上运行,执行并行计算任务。
What CPU does
• CPU allocates a block of memory on GPU
• CPU copies data from CPU to GPU
• CPU initiates launching kernels on GPU
• CPU copies results back from GPU to CPU
What GPU does
• GPU efficiently launch a lot of kernels
• GPU runs kernels in parallel
• A kernel looks like a serial C program for a thread
• The GPU will run the kernel for many threads in parallel
CPU和GPU之间的数据传输是一个瓶颈,应该尽量减少数据传输的次数和数据量。
第一个CUDA程序
我们以relu函数为例,展示如何编写一个简单的CUDA程序。
//relu on CPU
float relu_cpu(float x) {
return x > 0 ? x : 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
h_out[i] = relu_cpu(h_in[i]);
}
//relu on GPU
__global__ void relu_gpu(float* in, float* out) {
int i = threadIdx.x; // get thread index
out[i] = in[i] > 0 ? in[i] : 0;
}
relu_gpu<<<1, N>>>(d_in, d_out);
两种模块的执行方式:
CPU代码:
// CPU code
const int N = 64;
const int size = N * sizeof(float);
// allocate memory on CPU
float* h_in = (float*) malloc(size);
float* h_out = (float*) malloc(size);
// initialize input array
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
h_in[i] = (i - 32) * 0.1;
}
// relu on CPU
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
h_out[i] = relu_cpu(h_in[i]);
}
// free memory ...
GPU代码:
// GPU code
// 1. allocate memory on GPU
float* d_in = nullptr;
float* d_out = nullptr;
cudaMalloc(&d_in, size);
cudaMalloc(&d_out, size);
// 2. copy data from CPU to GPU
cudaMemcpy(d_in, h_in, size,
cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
// 3. launch the kernel
relu_gpu<<<1, N>>>(d_in, d_out);
// 4. copy data from GPU to CPU
cudaMemcpy(h_out, d_out, size,
cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
// free memory ...
CUDA函数的调用方式:
kernel<<<numBlocks, blockSize>>>(args);
// numBlocks: number of blocks
// blockSize: number of threads per block, typically 256 512 or 1024
// 一般会固定blockSize,然后根据数据量计算numBlocks
numBlocks传入的参数实际上是
dim3(x,y,z)结构体,可以指定三维的网格结构。
实现一个更通用的relu函数
Kernel «< number of blocks, number of thread per block »> (…)
// Use 512 or 256 threads per block
const int kCudaThreadsNum = 512;
inline int CudaGetBlocks(const int N) {
return (N + kCudaThreadsNum - 1) / kCudaThreadsNum;
}
// Define the grid stride looping
#define CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(i, n)
for (int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
i < (n);
i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x)
__global__ void relu_gpu(float* in, float* out, int n) {
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(i, n) {
out[i] = in[i] > 0 ? in[i] : 0;
}
}
relu_gpu <<<CudaGetBlocks(N), kCudaThreadsNum>>> (
d_in, d_out, N);
Tensor
Tensor是一个多维数组,可以看作是矩阵的推广。
Tensor是在CPU或GPU上一段连续的内存空间。
Tensor的成员变量:
- sizes:表示每个维度的大小
- strides:表示每个维度的步长
- dtype:表示数据类型
- device:表示存储设备(CPU或GPU)
Tensor的索引计算
假设有一个3维的Tensor,大小为(2, 3, 4),步长为(12, 4, 1),要访问元素(1, 2, 3),索引计算如下:
\[\text{index} = 1 \times 12 + 2 \times 4 + 3 \times 1 = 12 + 8 + 3 = 23\]这里的公式使用了标准的 LaTeX 语法(\times 代替 _),并且添加了等号和最终结果,符合数学排版规范。npm run format 可能会自动修正不规范的 Markdown 或 LaTeX 语法,比如将 _替换为\times,以保证公式的正确渲染和一致性。
对于切片操作,实际上是构建了一个新的Tensor,新的Tensor共享原始Tensor的内存,只是修改了sizes和strides,并且记录了一个offset,表示切片的起始位置。
但是切片操作可能会导致内存不连续,影响性能,有的时候可能需要构建一个新的Tensor。
对于reshape操作,如果新的形状和原始形状的内存布局不冲突,可以直接修改sizes和strides,否则需要重新分配内存并复制数据。
因此这些直接修改sizes和strides的操作,使用代价都很低。
GPU内存管理
GPU的内存可以分为全局内存(Global Memory)、共享内存(Shared Memory)和本地内存(Local Memory)。其中,全局内存是所有线程块共享的,访问速度较慢;共享内存是线程块内的线程共享的,访问速度较快;本地内存是每个线程私有的,访问速度最快。
CPU的内存只能与GPU的全局内存进行交互。
__global__ foo(float* x, float* y) {
int i = threadIdx.x; // local memory
float s, t; // local memory
__shared__ float s[128]; // shared memory
__shared__ float a, b, c; // shared memory
// which of the following is the fastest?
t = *x;
b = a;
s[i] = t;
*y = *x;
}
// t is in local memory, a and b are in shared memory, s is in shared memory, x and y are in global memory
// accessing local memory is the fastest, accessing shared memory is faster than accessing global memory
// accessing global memory is the slowest
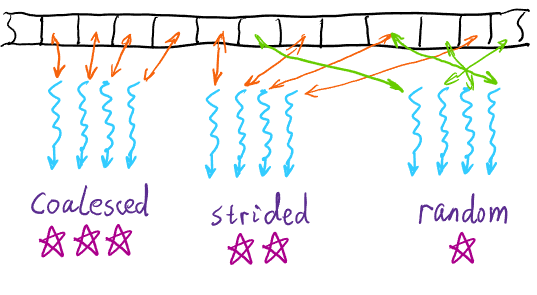
内存访问的一致性(Memory Coalescing)
为了提高内存访问的效率,应该尽量让线程访问连续的内存地址,这样可以利用内存的带宽,提高访问速度。
__global__ foo(float* x) {
int i = threadIdx.x; // local memory
float s, t; // local memory
// which of the following is coalesced?
t = x[i];
x[i*2] = t; // not coalesced 避免
x[i+1] = s;
}
因此,在设计数据结构和访问模式时,应该考虑内存访问的一致性。比如慎重使用Hash等数据结构。
总结
• Reduce frequent data transmission between GPU and CPU
• Reduce frequent memory visit of global memory
• Use shared memory to reduce the visit of global memory
• Prefer coalesced global memory access
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: